Wireless power transfer (WPT), wireless power transmission, wireless energy transmission (WET), or electromagnetic power transfer is the transmission of electrical energy without wires as a physical link. In a wireless power transmission system, a transmitter device, driven by electric power from a power source, generates a time-varying electromagnetic field, which transmits power across space to a receiver device, which extracts power from the field and supplies it to an electrical load. Wireless power transfer is useful to power electrical devices where interconnecting wires are inconvenient, hazardous, or are not possible.
Wireless Power Technology has always been surrounded skepticism and with this topic, we look to provide you a Holistic view of WPT which most of the common population still think to be more of a Myth than a Reality.
Wireless power techniques mainly fall into two categories, near field and far-field. In near field or non-radiative techniques, power is transferred over short distances by magnetic fields using inductive coupling between coils of wire, or by electric fields using capacitive coupling between metal electrodes. Inductive coupling is the most widely used wireless technology; its applications include charging handheld devices like phones and electric toothbrushes, RFID tags, and wirelessly charging or continuous wireless power transfer in implantable medical devices like artificial cardiac pacemakers, or electric vehicles.
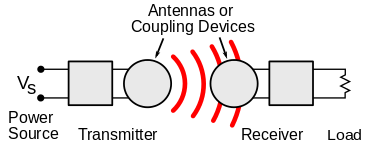
In far-field or radiative techniques, also called power beaming, power is transferred by beams of electromagnetic radiation, like microwaves or laser beams. These techniques can transport energy longer distances but must be aimed at the receiver. Pro
posed applications for this type are solar power satellites, and wireless powered drone aircraft.
Wireless power transfer - Overview
Wireless power transfer is a generic term for a number of different technologies for transmitting energy by means of electromagnetic fields.The technologies differ in the distance over which they can transfer power efficiently, whether the transmitter must be aimed (directed) at the receiver, and in the type of electromagnetic energy they use: time varying electric fields, magnetic fields, radio waves, microwaves, infrared or visible light waves.
In general a wireless power system consists of a "transmitter" device connected to a source of power such as a mains power line, which converts the power to a time-varying electromagnetic field, and one or more "receiver" devices which receive the power and convert it back to DC or AC electric current which is used by an electrical load. At the transmitter the input power is converted to an oscillating electromagnetic field by some type of "antenna" device. The word "antenna" is used loosely here; it may be a coil of wire which generates a magnetic field, a metal plate which generates an electric field, an antenna which radiates radio waves, or a laser which generates light. A similar antenna or coupling device at the receiver converts the oscillating fields to an electric current. An important parameter that determines the type of waves is the frequency, which determines the wavelength.
Wireless power uses the same fields and waves as wireless communication devices like radio, another familiar technology that involves electrical energy transmitted without wires by electromagnetic fields, used in cellphones, radio and television broadcasting, and WiFi. In radio communication the goal is the transmission of information, so the amount of power reaching the receiver is not so important, as long as it is sufficient that the information can be received intelligibly. In wireless communication technologies only tiny amounts of power reach the receiver. In contrast, with wireless power the amount of energy received is the important thing, so the efficiency (fraction of transmitted energy that is received) is the more significant parameter. For this reason, wireless power technologies are likely to be more limited by distance than wireless communication technologies.
Wireless power transfer may be used to power up wireless information transmitters or receivers. This type of communication is known as wireless powered communication (WPC). When the harvested power is used to supply the power of wireless information transmitters, the network is known as Simultaneous Wireless Information and Power Transfer (SWIPT); whereas when it is used to supply the power of wireless information receivers, it is known as a Wireless Powered Communication Network (WPCN).
In the United States, the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) provided its first certification for a wireless transmission charging system in December 2017.
Types of Wireless Power Transmission Methods:
There are different types of wireless power transmission methods: microwave power transmission, inductive-coupling-power transmission and laser-power transmission methods.
1. Microwave Power Transmission
William C Brown, the pioneer in the WPT technology, has designed and exhibited to show how power can be transmitted through free space by microwaves. The concept of the WPT is explained with a functional block diagram which is shown below.
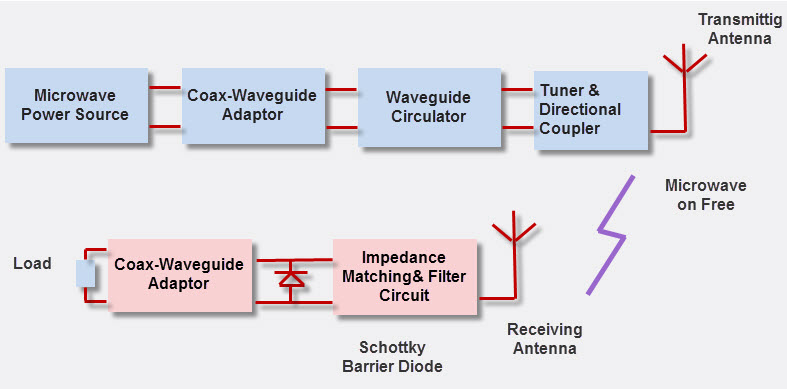
The functional block diagram of WPT consists of two sections: transmitting section and receiving section. In the transmission section, the microwave power source generates microwave power which is controlled by the electronic control circuits. The waveguide circulator protects the microwave source from the reflected power, which is connected through the co-ax waveguide adaptor. The tuner contests the impedance between the microwave source and transmitting antenna. Then, based on the signal propagation direction, the attenuated signals are separated by the directional coupler. The transmitting antenna emits the power regularly through free space to the receiving antenna.
In the receiving section, the receiving antenna receives the transmitted power and converts the microwave power into DC power. The filter and impedance matching circuit is provided for setting the output impedance of a signal source which is equal to rectifying circuit. This circuit consists of Schottky barrier diodes which converts the received microwave power into DC power.
2. Inductive Coupling Power Transmission: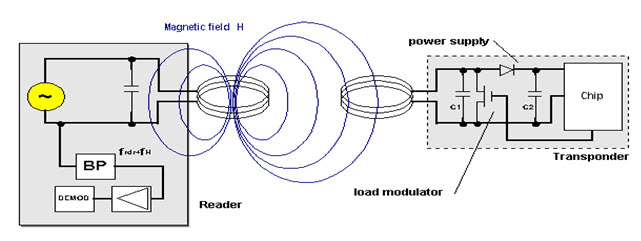
Inductive coupling method is the most important methods transferring energy wirelessly through inductive coupling. Basically, it is used for near -field power transmission. The power transmission takes place between the two conductive materials through mutual inductance. The general example of inductive coupling power transmission is a transformer.
3. Laser Power Transmission: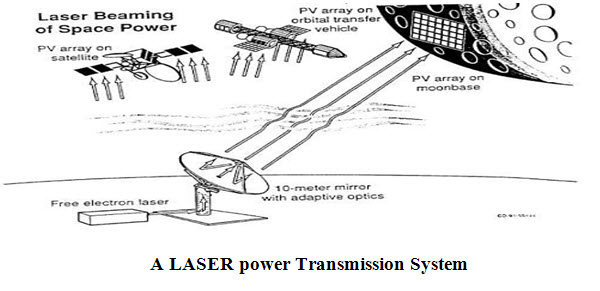
In this type of power transmission method, a LASER is used to transfer power in the form of light energy, and the power is converted to electric energy at the receiver end. The LASER gets powered using different sources like sun, electricity generator or high-intensity-focused light. The size and shape of the beam are decided by a set of optics. The transmitted LASER light is received by the photo-voltaic cells, that converts the light into electrical signals. Usually, it uses optical-fiber cables for transmission.
Applications of Wireless Power Transmission (WPT
Several applications of wireless power transfer are apparent and obvious. Firstly, WPT could eliminate traditional charging systems in place today. Instead of plugging in a mobile phone or laptop via power cord to charge the battery, wireless power can be harnessed and implemented in a home such that a laptop and phone charge continuously and wirelessly without the need for plugging anything in. Higher level applications include charging of electric vehicles (EVs). As EVs become more and more prevalent on the roads, the feasibility of driving such a vehicle can be maximized via stationary, and even mobile, WPT systems. Future and theoretical applications include a potential solution to renewable energy for the planet, by means of satellites collecting sunlight and sending power back to earth through MPT. Applications of WPT are described in this section.
Electronic portable devices
Cell phones, laptops, tablets, even smart watches are found all over the globe and are owned and used by billions of people. What these devices all have in common is the need to recharge their internal battery so that the device can be used while mobile. Such is the paradox of portable devices: they provide convenience by running off internal power so they can be used anywhere, but always must return to be tethered to a power cord in order to charge.
WPT has the potential to disrupt and revolutionize the traditional portable device, not only by making mobile devices more convenient by eliminating the need for a physical power supply, but also safer (power cords carry risk of shock and can cause fires), as well as a reduced cost for consumers. Research has even been done into multi-hop WPT systems, wherein a generator transmits power wirelessly to targets, which can then in turn become sources for other targets, and transfer power wirelessly to those targets. Thus, a network of WPT can be created to support several devices.
Electric Vehicles
As concern over global warming and greenhouse gas emissions grows across the globe, the prevalence of electric vehicles has also increased. One of the drawbacks of electric vehicles is their battery. Electric vehicles currently need to be plugged in to recharge their internal batteries, and take many hours to do so. However, many envision that in the near future, one need only park her car in a pre-determined spot in her driveway and the car will charge wirelessly and automatically. Thus a great deal of research has been done into WPT, specifically through the MPT mechanism, and how it can be used for the charging of electric vehicles.
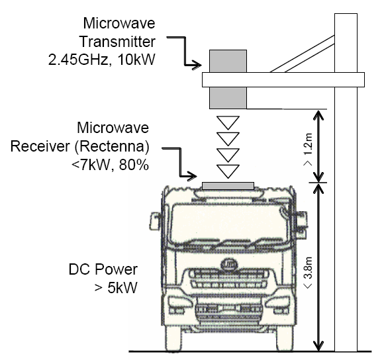
MPT charging of electric vehicles, specifically a system for charging electric trucks. As shown in Figure - an electric truck has a rectenna on its roof, and an MPT system can be created such that when an electric truck parks beneath the microwave transmitter, the rectenna converts the microwave radiation to DC to charge the vehicle.
In particular, the transmitter emits 10kW power through microwaves at 2.45 GHz, and the rectenna converts those microwaves with an efficiency of greater than 80%, yielding more than 7kW to the electric vehicle. Accounting for other losses through the charging of the system, the battery is able to receive more than 5kW power. The figure depicts a practical application of MPT. Importantly, the MPT system depicted has a high density with respect to the forming of the beam, and since the beam is highly focused, thus it does not create a large area of microwave radiation which could potentially be unsafe for human exposure.
Wireless Power Transmission - Future Trends
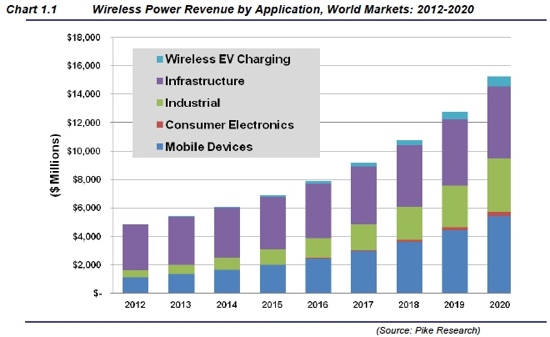
According to the new market research report - Wireless Power Transmission Marketby Technology (Induction, Magnetic Resonance), Implementation, Transmitter, and Receiver Application (Smartphones, Electric Vehicles, Wearable Electronics, and Furniture) and Geography - Global Forecast to 2022, the wireless power transmission market is expected to be worth USD 11.27 Billion by 2022, growing at a CAGR of 23.15% between 2018 and 2022.
The factors that are driving the growth of the wireless power transmission market include the convenience offered by and consumer preference for wireless connectivity and need for effective charging systems. The market has also witnessed significant developments for wireless charging as many start-ups have developed the products based on laser and microwave technologies, which can charge multiple devices at a time.
Wireless Power Transmission - Benefits
Benefits of WPT:
- WPT system completely reduces existing high-tension power transmission cables, substations and towers between the consumers and generating station.
- The cost of the distribution and transmission become less.
- The cost of the electrical energy to the consumers also reduces.
- The power could be transmitted to places to which the wired transmission is not possible.
Future Trends: Aerial Vehicles and Solar Power Satellites
While portable device and vehicle charging are applications are already under practical implementation, some of the future usage of Wireless Power Transfer applications have been placed for further research and development.
Aerial Vehicles
One such Aerial Vehicle application is the Stationary High Altitude Relay Platform (SHARP). The SHARP system consists of an unmanned airplane that flies at an altitude of approximately 13 miles above the earth, constantly circling the earth in a 2 kilometer diameter. The SHARP airplane would then be used as a communications relay. Here, the SHARP airplane has a large rectenna behind the wings, allowing for power to be transmitted to it from the earth, and thus is able to stay in the air for long periods of time, potentially months A picture of the aircraft is shown in the Image.
Solar Powered Satellites
A solar power satellite (SPS) is a renewable energy system that converts the sun's energy into electricity in space and transmits it to Earth using microwaves. The SPS concept, first proposed in 1968 in the United States, has recently started attracting increased public attention as a promising energy system that can be used to resolve global environmental and energy problems. One of the most challenging technologies for the SPS is microwave power transmission from the geostationary orbit to the ground. The technologies for microwave power transmission have been studied for more than 40 years since the initial demonstrations in the 1960s; however, for SPS application, considerable research, especially on high-efficiency power conversion between direct current (dc) and radio frequency (RF) and on high-accuracy microwave beam control over a long range, is still needed. Current research status and the future development prospects for microwave power transmission towards commercial SPS use are also described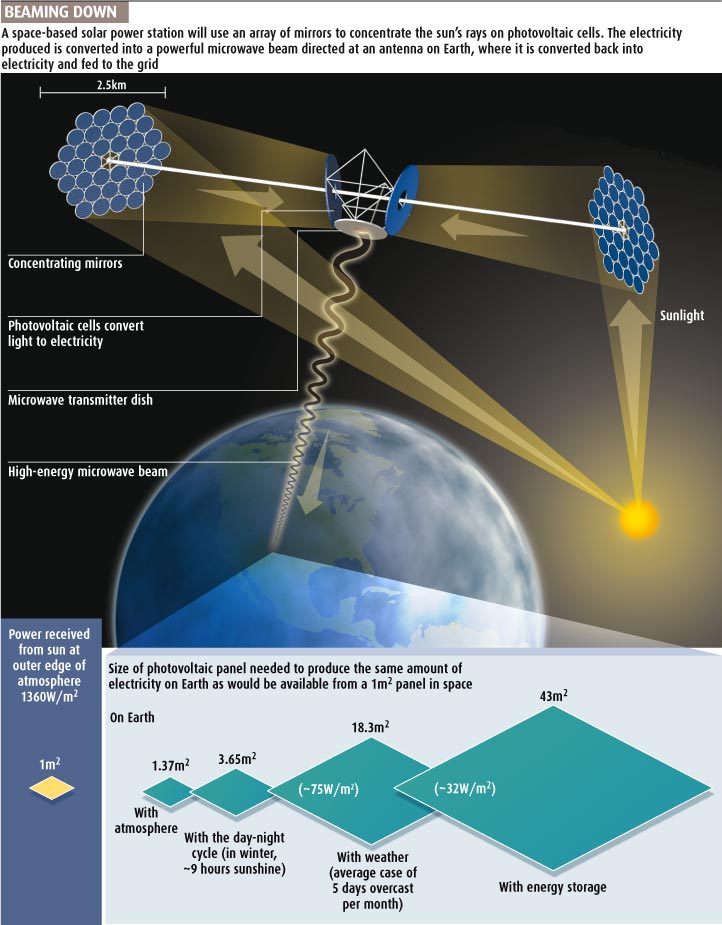
Carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions from burning fossil fuels have become a point of great concern with respect to global warming. Additionally, fossil fuels are a nonrenewable energy source, and by some estimates fossil fuels could be completely consumed in 100 to 150 years. Thus the need for clean, safe, and abundant renewable energy has been a topic of much debate and recent study. Current renewable energy systems have many drawbacks; solar cells are constrained by the weather, most significantly by cloud cover and lack of sunlight during the night. Wind turbines are contingent upon weather as well, and do not function when no wind is present. Nuclear power plants produce toxic waste and have the potential to cause great disasters in the event of a nuclear meltdown.
The SPS, on the other hand is a different system entirely, with the collection of solar power unconstrained by environmental factors. In the SPS system, a satellite is fixed in a geostationary orbit above the earth. This satellite collects solar energy and, using the MPT mechanism, beams the energy back down to the earth via microwaves where it is received and converted to power at a rectenna of a size of approximately 2 km2 and then transfers that energy to existing power grids. A satellite above the earth is superior to ground based solar power harvesting because it is unaffected by the weather and is unconstrained by lack of sunlight during night hours, and thus can collect solar energy continuously. Even after accounting for loss during conversion of power to and from microwaves, the SPS system is still able to deliver more power than ground based solar panels. For example, solar radiation has been measured on the ground in Tokyo, Japan as approximately 140 W/m2, whereas a satellite in space can collect solar energy that is measured as 1400 W/m2.
Conclusion
The SHARP and SPS systems are both practical implementations of WPT via the MPT mechanism. Indeed, both systems are simply MPT systems, just scaled to a larger size. They consist of a microwave generator that converts power to microwaves and sends those microwaves to a target rectenna that converts the microwaves back to DC power to be used by the target system.
About the Author The writer of this article is a Research and Technology Enthusiast. His core area of research is Information Technology, Robotics and Artificial Intelligence.Sources: Wireles Power - Introduction: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wireless_power_transfer Types of Wireless Power Transmission: https://www.efxkits.us/wireless-power-transmission-technology/ Wireless Power Transmission Market Trends: https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/PressReleases/wireless-power-transmission.asp














Leave a Reply