INTRODUCTION
Security is freedom from, or resilience against, potential harm (or other unwanted coercive change) caused by others. Beneficiaries (technically referents) of security may be of persons and social groups, objects and institutions, ecosystems or any other entity or phenomenon vulnerable to unwanted change.
Security mostly refers to protection from hostile forces, but it has a wide range of other senses: for example, as the absence of harm (e.g. freedom from want); as the presence of an essential good (e.g. food security); as resilience against potential damage or harm (e.g. secure foundations); as secrecy (e.g. a secure telephone line); as containment (e.g. a secure room or cell); and as a state of mind (e.g. emotional security).
TYPES OF SECURITY
| TECHNOLOGY SECURITY | HUMAN SECURITY | POLITICAL SECURITY | MONETARY SECURITY |
| Communication Security | Physical Security | National Security | Economic Security |
| Computer Security | Airport Security | Public Security | Financial Security |
| Internet Security | Corporate Security | Homeland Security | Social Security |
| Application Security | Food Security | Internal Security | |
| Data Security | Environmental Security | International Security | |
| Digital Security | Home Security | Global Security | |
| Information Security | Physical Security | Community Security | |
| Network Security | Personal Security | ||
| Endpoint Security | Infrastructure Security | ||
| Supply Chain Security | |||
| Port Security |
TECHNOLOGY SECURITY
 IT security is a set of cyber-security strategies that prevents unauthorized access to organizational assets such as computers, networks, and data. It maintains the integrity and confidentiality of sensitive information, blocking the access of sophisticated hackers.
IT security is a set of cyber-security strategies that prevents unauthorized access to organizational assets such as computers, networks, and data. It maintains the integrity and confidentiality of sensitive information, blocking the access of sophisticated hackers.
Network security
Network security is used to prevent unauthorized or malicious users from getting inside your network. This ensures that usability, reliability, and integrity are uncompromised. This type of security is necessary to prevent a hacker from accessing data inside the network. It also prevents them from negatively affecting your users’ ability to access or use the network.
Network security has become increasingly challenging as businesses increase the number of endpoints and migrate services to public cloud.
Internet security
Internet security involves the protection of information that is sent and received in browsers, as well as network security involving web-based applications. These protections are designed to monitor incoming internet traffic for malware as well as unwanted traffic. This protection may come in the form of firewalls, antimalware, and antispyware.
Endpoint security
Endpoint security provides protection at the device level. Devices that may be secured by endpoint security include cell phones, tablets, laptops, and desktop computers. Endpoint security will prevent your devices from accessing malicious networks that may be a threat to your organization. Advance malware protection and device management software are examples of endpoint security.
Cloud security
Applications, data, and identities are moving to the cloud, meaning users are connecting directly to the Internet and are not protected by the traditional security stack. Cloud security can help secure the usage of software-as-a-service (SaaS) applications and the public cloud. A cloud-access security broker (CASB), secure Internet gateway (SIG), and cloud-based unified threat management (UTM) can be used for cloud security.
Application security
With application security, applications are specifically coded at the time of their creation to be as secure as possible, to help ensure they are not vulnerable to attacks. This added layer of security involves evaluating the code of an app and identifying the vulnerabilities that may exist within the software.
HUMAN SECURITY
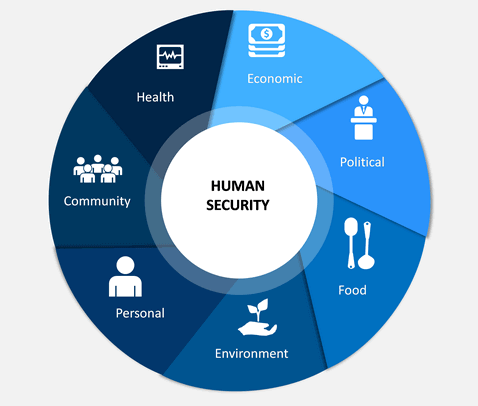 The concept of human security emanates from the conventional security studies which centers on the security of the state. Its focus is individuals and its ultimate end point is the protection of people from traditional and non-traditional threats. Centre to this concept is the belief that human security deprivations can undercut peace and stability within and among states.
The concept of human security emanates from the conventional security studies which centers on the security of the state. Its focus is individuals and its ultimate end point is the protection of people from traditional and non-traditional threats. Centre to this concept is the belief that human security deprivations can undercut peace and stability within and among states. POLITICAL - Global AND National Security
 Nations of the world prioritize the safety of its territorial integrity, resources and its entire citizenry. This informs the belief that national security is the preservation of independence and sovereignty of a nation state. In reality, every country has a large number of interests to protect. These interest put together constitute the national interest which originates from values, good governance and protection of social and economic well-being of the entire citizenry. Based on this, one may describe national security as the protection and maintenance of national interest of a state or nation(s).
Nations of the world prioritize the safety of its territorial integrity, resources and its entire citizenry. This informs the belief that national security is the preservation of independence and sovereignty of a nation state. In reality, every country has a large number of interests to protect. These interest put together constitute the national interest which originates from values, good governance and protection of social and economic well-being of the entire citizenry. Based on this, one may describe national security as the protection and maintenance of national interest of a state or nation(s).MONETARY SECURITY (Finance)
According to Verified Market Research, The Global Physical Security Market was valued at USD 85.58 billion in 2017 and is projected to reach USD 184.01 billion by 2025, growing at a CAGR of 10.1% from 2018 to 2025.Global Security - Market Analysis







 A security, in a financial context, is a certificate or other financial instrument that has monetary value and can be traded.
A security, in a financial context, is a certificate or other financial instrument that has monetary value and can be traded. 










Leave a Reply