Augmented Reality (AR) allows the user to see the real world, with virtual objects superimposed upon or composited with the real world by supplementing reality, rather than completely replacing it.” In simple words, Incorporating any kind of a computer generated content on top of an existing real-life environment is called Augmented Reality.
Brief History:
The term Augmented reality was coined by the Thomas Caudell, a Boeing researcher.
1960s. In 1968 Ivan Sutherland and Bob Sproull created a first head-mounted display, they called it "The Sword of Damocles". Obviously, it was a rough device that displayed primitive computer graphics. 1970s. In 1975 Myron Krueger created Videoplace – an artificial reality laboratory. The scientist envisioned the interaction with digital stuff by human movements. This concept later was used for certain projectors, video cameras and onscreen silhouettes. 1980s. In 1980 Steve Mann developed a first portable computer called EyeTap, designed to be worn in front of the eye. It recorded the scene to superimposed effects on it later, and show it all to a user who could also play with it via head movements. In 1987 Douglas George and Robert Morris developed the prototype of a heads-up display (HUD). It displayed astronomical data over the real sky. 1990s. Year 1990 marked the birth of the “augmented reality” term. It first appeared in the work of Thomas Caudell and David Mizell – Boeing company researchers. In 1992 Louis Rosenberg of the US Air Force created the AR system called “Virtual Fixtures”. In 1999, a group of scientists led by Frank Delgado and Mike Abernathy tested new navigation software, which generated runways and streets data from a helicopter video. 2000s. In 2000 a Japanese scientist Hirokazu Kato developed and published ARToolKit – an open-source SDK. Later it was adjusted to work with Adobe. In 2004 Trimble Navigation presented an outdoor helmet-mounted AR system. In 2008 Wikitude made the AR Travel Guide for Android mobile devices.
AR today. In 2013 Google beta tested the Google Glass – with internet connection via a Bluetooth. In 2015 Microsoft presented two brand new technologies: Windows Holographic and HoloLens (an AR goggles with lots of sensors to display HD holograms). In 2016 Niantic launched Pokemon Go game for mobile devices. The app blew the gaming industry up and earned $2 million in just first week.
Augmented Reality - In detail
Augmented Reality (AR) is a computational technique purely based on visualization, An AR visualization is comprised of three main features:
- Combination of the real and virtual world.
- Real-time interaction.
- Rendering content in 3 dimensions.
With its interactive and preferable virtual content, AR has been prevalent in the recent days in fields like education, advertising, entertainment. It is estimated that as of 2017, a whopping 2.5 billion mobile AR applications are being used universally.
How does Augmented Reality work
For AR a certain range of data (images, animations, videos, 3D models) may be used and people will see the result in both natural and synthetic light. Also, users are aware of being in the real world which is advanced by computer vision, unlike in VR. AR can be displayed on various devices: screens, glasses, handheld devices, mobile phones, head-mounted displays. It involves technologies like S.L.A.M. (simultaneous localization and mapping), depth tracking (briefly, a sensor data calculating the distance to the objects), and the following components:
- Cameras and sensors. Collecting data about user’s interactions and sending it for processing. Cameras on devices are scanning the surroundings and with this info a device locates physical objects and generates 3D models. It may be special duty cameras, like in Microsoft Hololens, or common smartphone cameras to take pictures/videos.
- Processing. AR devices eventually should act like little computers, something modern smartphones already do. In the same manner, they require a CPU, a GPU, flash memory, RAM, Bluetooth/WiFi, a GPS, etc. to be able to measure speed, angle, direction, orientation in space, and so on.
- Projection. This refers to a miniature projector on AR headsets, which takes data from sensors and projects digital content (result of processing) onto a surface to view. In fact, the use of projections in AR has not been fully invented yet to use it in commercial products or services.
- Reflection. Some AR devices have mirrors to assist human eyes to view virtual images. Some have an “array of small curved mirrors” and some have a double-sided mirror to reflect light to a camera and to a user’s eye. The goal of such reflection paths is to perform a proper image alignment.
Components of Augmented Reality:
As most systems Augmented Reality setup consists of devices such as a processor, display, input devices, and sensors. The display is either a monitor, handheld device, eyeglass or Head Mounted Display.
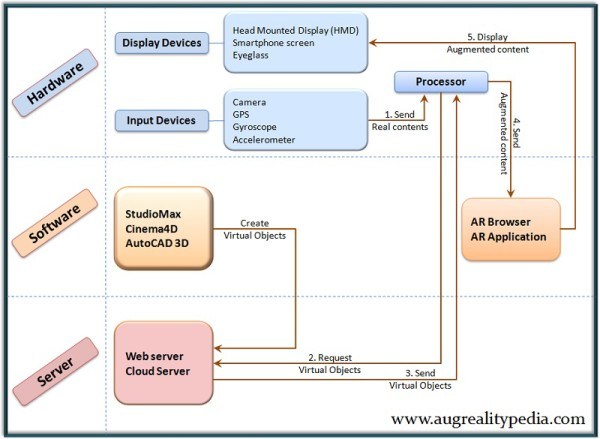
Classification:
Based on the fields in which they are operated or applied AR applications are classified into the following types some of which are critically important and the others are extensions of the same.
- Marker-based AR. Some also call it image recognition, as it requires a special visual object and a camera to scan it. It may be anything, from a printed QR code to special signs. The AR device also calculates the position and orientation of a marker to position the content, in some cases. Thus, a marker initiates digital animations for users to view, and so images in a magazine may turn into 3D models.
- Markerless AR. A.k.a. location-based, or position-based augmented reality, that utilizes a GPS, a compass, a gyroscope and an accelerometer to provide data based on user’s location. This data then determines what AR content you find or get in a certain area. With availability of smartphones this type of AR typically produces maps and directions, nearby businesses info. Applications include events and information, business ads pop-ups, navigation support.
- Superimposition-based AR. Replaces the original view with an augmented, fully or partially. Object recognition plays a key role, without it the whole concept is simply impossible. We’ve all seen the example of superimposed augmented reality in IKEA Catalog app, that allows users to place virtual items of their furniture catalog in their rooms.
- Projection-based AR. Projecting synthetic light to physical surfaces, and in some cases allows to interact with it. These are the holograms we have all seen in sci-fi movies like Star Wars. It detects user interaction with a projection by its alterations.
Applications:
Augmented reality and Big Data have introduced new business rules. But not all the businesses are able to implement this collaborative visualization technique due to the inadequacy or limited data. Though there are only limited markets where this visualization is applicable, it is evident that it might go far beyond.
Medicine / Education:
Applications based on human anatomy exist in the real world which helps medical students and also common people to understand the human anatomy just by pointing at a body part and scanning it through the app. This kind of application can be extended to a greater extent in education in many areas of interest where interactive training is necessary.
Retail:
Augmented Reality has also influenced the retail markets but is limited in some geographical areas. AR-enabled layers overlay information on the existing screen by taking the environment into consideration In the United States IKEA is one of the retailers which has implemented AR into its mobile application which virtually places a furniture item in the customer’s house or office to match the surroundings.
Gaming:
Game development and gaming applications is another area where augmented reality is on the rise. Games which augmented reality incorporated into them has been a huge hit. For instance, Pokemon Go! from Nintendo which used the real-time geographical information to render the game content on the mobile devices was really appreciated and acclaimed by the world.
Tourism:
Tourism is another sector where AR is widely associated. Large data sets are generated from spatial exploration, GPS based tracking, analyzing trends from tweets or check-ins, surveys etc. which can be used to analyze and provide the customers with an interactive tour planner /guide. Geographical data is also being used to develop interactive 3-D maps for improved navigation systems.
Augmented Reality and its applications: Past, Present, Future "The sword of Damocles"
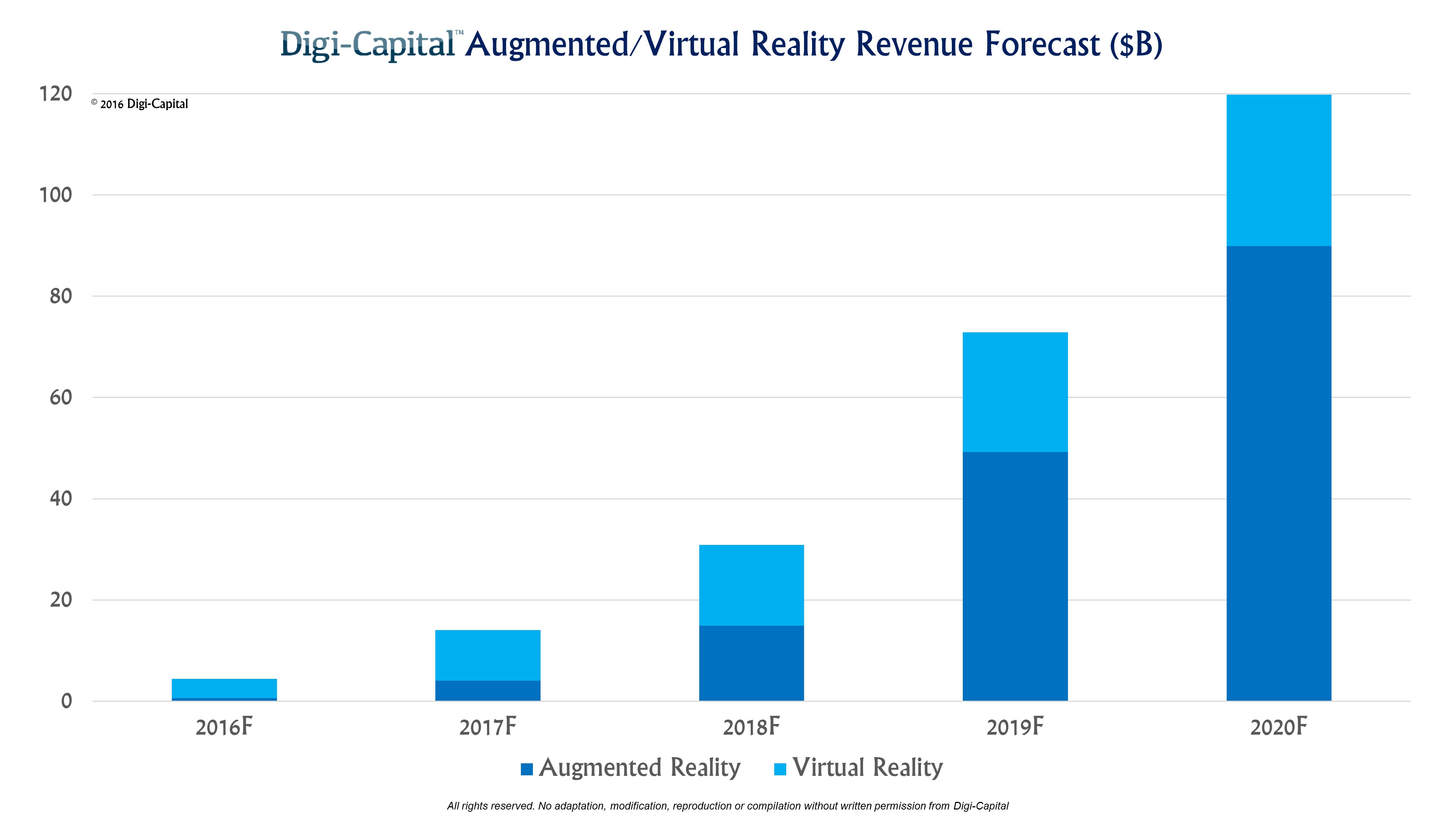
As the computing power of the handheld devices in our environment is improving, the future of Augmented reality is bright. In the present day, AR has made its own impact in the entertainment, Sports, Tourism and many other industries which have the visualization in them. Similarly, there is much scope for many other industries to research, experiment and adopt the technology. The below graphical representation shows us a forecast of the growth of AR in the coming days.
Conclusion:
Augmented Reality could enhance the way we design for people. It has proven that with the characteristic of AR, people could comprehend and appreciate design more thoroughly. Indeed with all the supporting resources and analysis. Augmented reality is an immersive data experience providing platform offering a broader scale for immersive visual experiences which a higher level of interaction to the end user.
About the Author - Ananth IyerThe writer of this article is a Ph.D. Student & Graduate Teaching Assistant for the Department Of Computer Science at The University of North Dakota.
Sources:[1]Azuma, Ronald T. "A survey of augmented reality." Presence: Teleoperators & Virtual Environments 6.4 (1997): 355-385 [2]Augmented Reality Archives - AugRealityPedia (ARP). (n.d.). Retrieved from https://www.augrealitypedia.com/augmented-reality/ [3]Augmented reality | Conclusion. (4041, 7). Retrieved from http://keanhwa.wixsite.com/augmentedreality/conclusion [4] Augmented Reality - Past, Present, Future. https://www.fastcompany.com/most-innovative-companies/2018/sectors/augmented-reality-virtual-reality [5] What is Augmented Reality. https://thinkmobiles.com/blog/what-is-augmented-reality/


















Leave a Reply