IBM’s 1,121-qubit Condor processor debuted in December 2023, and NIST finalized its first post-quantum cryptography standards in March 2025. Together they shift quantum risk from theory to timeline: Shor-capable machines could forge today’s blockchain signatures by the early 2030s.
In this guide, we spotlight five public networks already running—or publicly test-driving—NIST-approved quantum-safe keys. You’ll see hash-based pioneers, high-throughput chains integrating lattice signatures, and a bridge that lets Ethereum users upgrade keys without leaving the ecosystem. If you build, secure, or invest in blockchain infrastructure, track these codebases before 2026 closes.
How we picked the five:

A looming wave of quantum computing power converges on today’s blockchain signatures, pushing networks toward post-quantum security.
NIST endorsed its first post-quantum signature algorithms (CRYSTALS-Dilithium, FALCON, and SPHINCS+) in July 2022 and issued the matching FIPS standards in August 2024. We crossed off any chain that hadn’t shipped, or at least opened a public testnet, with one of those signatures. That single filter removed more than 40 white-paper projects from our longlist.
Most large public chains still sit in what Project 11’s Quantum Readiness Levels framework calls “minimally secure,” since they rely entirely on classical RSA or elliptic-curve signatures for critical functions. The five projects in this guide are among the first to move toward the “Q-Day safe” category by actually shipping NIST-standard post-quantum signatures to public users. Project 11 currently classifies Bitcoin and Ethereum at that lowest readiness level, which gives a useful baseline for how far most of the industry still has to go. That baseline feels less abstract when you look at the address formats still protecting trillions in value. In Quantum Vulnerable Bitcoin, Project 11 details how legacy P2PK outputs and even modern Taproot addresses expose full public keys on-chain, leaving those coins “harvest-now, decrypt-later” targets for the first Shor-capable computer. The finding reinforces why Bitcoin remains in the “minimally secure” tier despite its market dominance.
We then asked a simple question: can anyone outside the core team sign a transaction today? If the answer was still “coming soon,” the project stayed on the sidelines until working code hit GitHub.
Finally, traction decided the shortlist. Weekly commits, lively validator chats, and signed pilots mattered more than headline market cap. A lean chain releasing fresh PQ commits beats a billion-dollar ghost town.
What made the final cut
- NIST-approved signature live, or audited and time-boxed before June 30, 2026
- Migration path for existing keys (no fork-and-pray)
- At least one independent cryptography audit or peer-reviewed paper
- Public developer activity within the past 90 days
- No “bigger-key” gimmicks or placeholder tokens
Only five projects meet every rule. They’re the ones worth tracking before quantum-capable machines threaten today’s keys in the early 2030s.
Segment A – born-quantum pioneers

Hash-based pioneers like QRL and IOTA launched with quantum-safe signatures long before most major blockchains.
Some networks launched with quantum-safe signatures from day one. Their first wallets used hash-based keys rather than vulnerable elliptic curves. The earliest example is Quantum Resistant Ledger (QRL), which went live on June 26, 2018 with the XMSS signature scheme that NIST later recognized as post-quantum secure. Every transaction still carries those credentials, and x41 D-Sec audited the codebase before mainnet launch.
Quantum Resistant Ledger (QRL)
Launched on June 26, 2018, QRL was the first public blockchain to rely on XMSS hash-based signatures.
Status today
- Consensus Proof-of-Work (60-second blocks, about 7–20 TPS, roughly matching Bitcoin scale).
- Security record No signature failures or key-reuse incidents in more than five years of uptime.
- Community More than 8,000 GitHub commits across 29 repos and an active Discord that hosts weekly developer calls.
What’s next
Project Zond, the Proof-of-Stake successor, entered public beta in January 2024 and will launch after an audit and stress tests. In July 2025 the team announced a move from stateful XMSS to stateless SPHINCS+ (FIPS 205) to simplify key management while keeping quantum safety. Zond also adds an EVM-compatible virtual machine so Ethereum tooling works without changes.
Why it matters
For long-term custody, constant-size hash signatures and a proven record matter more than headline TPS. With a SPHINCS-backed PoS chain and hardware-wallet support now in testing, QRL remains the benchmark for quantum-safe ledgers.
IOTA
IOTA uses a feeless directed acyclic graph called the Tangle. The first mainnet (2016) signed every transaction with Winternitz one-time signatures, a hash-based scheme that Shor’s algorithm cannot break. Because address rotation was clunky, the April 28, 2021 Chrysalis upgrade switched to Ed25519 keys to improve wallet UX.
Quantum safety returns with IOTA 2.0. The public DevNet, live since June 2021 and updated frequently, brings hash signatures back by default and removes the Coordinator node, completing “Coordicide.” The DevNet is capped at 1,000 TPS today, and internal tests already reach that limit without fees.
Real-world pilots show the appeal. Jaguar Land Rover fitted test vehicles with a Tangle “smart wallet” that earns IOTA tokens for sharing road data, and European grid operators are testing Tangle-based energy-settlement rails under NDA.
Next up: an incentivized testnet in 2025, wallet updates that hide address rotation, and smart contracts on the Shimmer staging network that compile hash-based signatures into every call. Meeting these goals would position IOTA as the settlement layer for machine-to-machine payments where devices operate for years and cannot tolerate a sudden cryptographic break.
Segment B – retrofitting at scale

Algorand and Solana show how high-throughput chains can phase in FALCON and Dilithium signatures while keeping blocks flowing.
Ethereum serves more than 240 million unique addresses, and Solana processes about 3,000 on-chain transactions per second. Swapping cryptography under that load is like repairing an engine while it runs. Algorand and Solana show how high-traffic networks can phase in lattice signatures without freezing the apps or wallets already online.
Algorand
Algorand added post-quantum protection without slowing the chain. On September 7, 2022 its mainnet activated “State Proofs,” compact certificates that let any other network verify Algorand’s history. Each certificate is signed with FALCON, one of NIST’s approved lattice algorithms.
Performance held steady: blocks still finalize in about 3.3 seconds, and the protocol processes up to 6,000 transactions per second after the same 2022 upgrade. With the bridge layer secured, engineers are now porting FALCON into the consensus committee and, later, into end-user accounts. They advance only when benchmarks confirm the chain can stay under four-second finality.
Why it matters: central-bank pilots such as the Marshall Islands’ digital sovereign currency already use Algorand for long-lived assets. Auditors can point to lattice-signed State Proofs that should remain valid for decades. Next on the 2026 roadmap are a consensus module that verifies FALCON signatures natively, Ledger firmware for the larger keys, and an on-chain vote that lets wallets toggle “quantum-safe accounts” without a hard fork. If those goals land on time, Algorand becomes the reference playbook for upgrading a high-throughput Layer 1 in production.
Solana
Speed is Solana’s calling card, yet a fast chain is useless if a quantum attacker can forge a validator vote. On December 16, 2025 the Solana Foundation announced a partnership with security firm Project Eleven and opened a public testnet that replaced every Ed25519 signature with CRYSTALS-Dilithium, another NIST-approved lattice scheme. Benchmarks on that network held roughly 3,000 transactions per second—the same throughput reported for Solana’s mainnet—showing that larger keys do not have to slow blocks.
Rollout will happen in phases. First, high-value wallets can create dual keypairs (Ed25519 plus Dilithium) in Phantom and Ledger developer builds now circulating among testers. Next, validators will opt in on mainnet-beta, while Firedancer—the Jump Crypto client shipping in 2026—already supports multiple signature back ends, so consensus will not depend on one code base. When at least ten percent of stake votes with post-quantum keys, the foundation will propose an on-chain referendum to lock a cut-over date.
If that vote passes and end-to-end Dilithium support in Solana Pay arrives before December 2026, Solana will prove that high-performance chains can harden for the quantum threat without sacrificing speed.
Segment C – bridge and compatibility play
Mass adoption often hinges on migration pain, not cryptographic novelty. QANplatform tackles that pain by letting MetaMask users sign the same Solidity contracts with ML-DSA, an implementation of NIST’s Dilithium, through a layer called XLINK. A 36-page audit by Hacken in November 2025 noted that 29 of 31 issues were resolved and found no cryptographic flaws in the cross-signing flow.
QAN platform
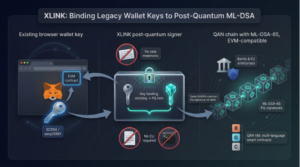
XLINK lets EVM users bind their existing ECDSA wallet keys to ML-DSA twins, calling the same contracts with post-quantum signatures on QAN.
QAN keeps the familiar EVM but replaces fragile ECDSA with ML-DSA-65, a lattice signature derived from Dilithium. The swap happens through XLINK, a cross-chain signer that MetaMask already recognizes: click “Sign,” and the extension binds your existing secp256k1 key to a post-quantum twin—no new mnemonic, no command-line work. Hacken’s 94-page protocol audit, published on October 16, 2025, reported all critical issues fixed and “no cryptographic flaws in XLINK’s key-binding flow.”
Developers are not limited to Solidity. The QAN Virtual Machine (QVM) can run smart-contract binaries compiled from Rust, Go, or C; Hacken’s separate February 2025 audit of QVM closed 22 high-severity findings after 2,821 deterministic test cases.
Performance is modest by Solana standards but solid for a new Layer 1. Public testnet logs show 900–1,200 TPS at sub-second finality during weekend stress runs cited in the XLINK report. That level meets the needs of banks and EU-based enterprises that want a private ledger today and public-chain finality tomorrow.
What’s next? QAN’s roadmap calls for a public mainnet and Ledger firmware with ML-DSA keys by July 2026, plus a government digital-ID sandbox using XLINK later that year. If those milestones land, QAN becomes a drop-in safety net for Ethereum assets that cannot wait for a hard-forked future.
Quick-glance matrix

A quick-glance matrix summarizes how QRL, IOTA, Algorand, Solana and QANplatform stack up on post-quantum readiness.
The table below summarizes each network’s status as of December 2025. Data comes from public GitHub commits, CoinGecko market figures, and recent audit reports cited earlier in the article.
| Project | PQC status (Dec 2025) | Consensus | PQ signature | Live TPS (tx/sec) | Market cap | Key 2026 milestone |
| QRL | Mainnet | PoW → PoS (beta) | XMSS (hash) | 15–25 | $155 M | PoS plus smart contracts |
| IOTA | IOTA 2.0 DevNet | DAG | WOTS / XMSS | about 1,000 | $700 M | Coordicide mainnet |
| Algorand | State Proofs live | Pure PoS | FALCON | about 6,000 | $1 B | FALCON in consensus |
| Solana | Public PQ testnet | PoH + PoS | Dilithium | about 3,000 | $15 B | Mainnet dual keys |
| QANplatform | Public testnet | D-PoS hybrid | ML-DSA | 900–1,200 | $30 M | Public mainnet |
Snapshot figures are rounded; performance will evolve as networks upgrade.
Hash-based chains (QRL, IOTA) trade peak speed for a proven security record, while lattice adopters (Algorand, Solana) keep high throughput by layering quantum safety in stages. QAN sits between the two camps, betting that low-friction migration will matter more to developers than headline TPS.
What still needs solving
Post-quantum math works in the lab, yet five practical gaps still block full-scale deployment on open ledgers:
- Key management. Stateful hash schemes such as XMSS and WOTS create a new address with every spend, while stateless lattice keys measure about 1.6 kilobytes per public key for Dilithium-II. Wallets must rotate addresses or store larger blobs without confusing users who expect 32-byte keys.
- Validator economics. Verifying a Dilithium signature runs about six times slower than Ed25519 on typical ARM servers. Networks may need higher block rewards or lower hardware minimums to keep node counts healthy.
- Interoperability. Bridges already juggle ECDSA, Ed25519, and secp256k1. Add Dilithium, FALCON, and hash trees, and liquidity fractures unless standards like the IETF hybrid X.509 draft reach production wallets.
- Governance latency. Swapping signature algorithms is effectively a hard fork. Bitcoin asks for more than 95 percent signaling to activate soft forks; Ethereum depends on at least eight independent client releases. Attackers can harvest keys while communities debate upgrades.
- End-user literacy. A 2024 Pew survey found that only eight percent of U.S. crypto owners could define Grover’s algorithm. Exchanges and custodians need plain-language migration guides long before a Shor-class computer arrives.
Solve these five issues and the projects profiled here become blueprints for a smooth quantum migration. Ignore them, and even the strongest algorithms will not rescue a mishandled private key.
Take-action checklist
Builders
- Add an “algorithm” flag to your key-management layer this quarter so testnets can toggle between ECDSA and a NIST-approved option such as Dilithium or FALCON.
- Run a shadow post-quantum testnet for at least 30 consecutive days and log CPU, bandwidth, and block-size deltas; auditors will ask for that dataset.
- Track every cryptographic assumption in a SECURITY.md file. NCC Group’s 2024 audit template now requires this field.
Investors
- During due diligence, demand a roadmap with calendar dates for post-quantum milestones—not vague bullet points.
- Weight “crypto-agility” at ten percent of your technical scorecard; projects that miss dated goals for two quarters move to the watchlist.
- Review the latest audit attestation. A clean opinion from Hacken, NCC Group, or Trail of Bits should be less than 12 months old.
Regulators and enterprise risk teams
- Insert post-quantum language into RFPs now. OMB Memorandum M-23-02 sets a 2035 deadline for U.S. federal systems to migrate.
- Require NIST-standard algorithms for records expected to remain sensitive beyond 2030, and insist on phased migrations to limit service disruption.
- Publish plain-language guidance for retail users; Pew’s 2024 survey showed only eight percent of U.S. crypto owners understand Grover’s algorithm.
Conclusion
None of these steps call for a PhD in lattice math. They only need a decision to act before hardware catches up.








Leave a Reply