Virtual reality is a technology which allows a user to view and interact with a rendered computer imagery in a three-dimensional environment where the interacting user becomes a part of the virtual world. The simplest form of virtual reality is a 3-D image that can be explored interactively at a personal computer, usually by manipulating keys or the mouse so that the content of the image moves in some direction or zooms in or out. More sophisticated efforts involve such approaches as wrap-around display screens, actual rooms augmented with wearable computers, and haptic devices that let you feel the display images.
History:
The Sensorama (1962) can be considered the first Virtual Reality device, it was a head-mounted display that played 3D film accompanied by sound, moving air, and aromas to create a virtual sensory environment was prototyped by Morton Heilig which was first thought of in a 1955 essay. This was a non-computerized VR followed later by computerized VR / AR.
[embed][/embed]A video about the Sensorama, the world’s first virtual reality device.
But it wasn't until 1987 that the term Virtual reality was first coined in, by Jaron Lanier, founder of the visual programming lab where he developed a range of virtual reality gear including the Dataglove in collaboration with Tom Zimmerman and the EyePhone head-mounted display. They were the first company to sell Virtual Reality goggles and gloves.
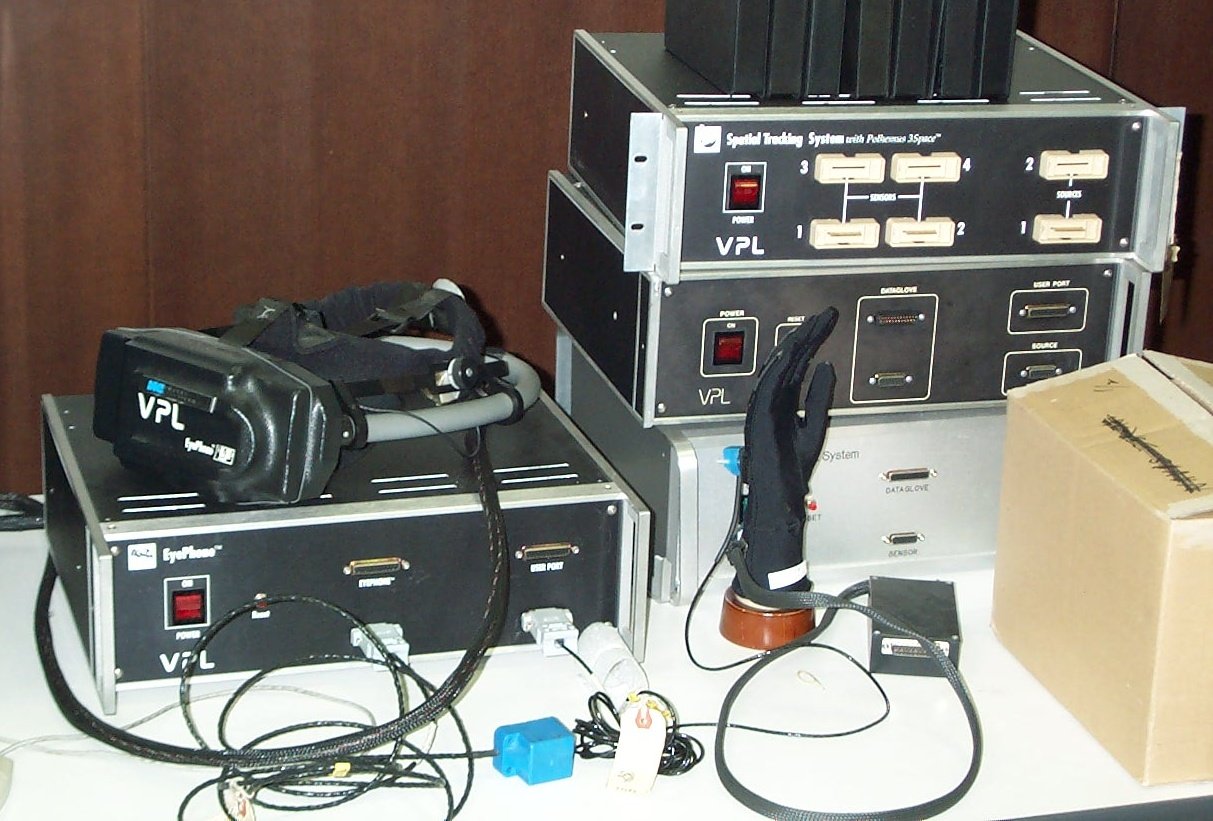

The above image shows us the data glove and the goggles developed by VPL which are considered to be the first VR devices.
Since the start of the 21st century, rapid advancements have been taking place in the field of virtual reality. Availability of high-performance portable devices, high definition displays, advanced graphics and rendering techniques have all added to the growth. The video game industry has continued to drive the development of consumer virtual reality unabated. Depth sensing cameras sensor suites, motion controllers, and natural human interfaces are already a part of daily human computing tasks.
Developer versions of final consumer products have also been available for a few years, so there has been a steady stream of software projects creating content for the immanent market entrance of modern virtual reality. After the release of Oculus Rift in 2016, many companies such as HTC, Microsoft, Sony and Google have introduced there own set of VR goggles and devices which is followed by many other smaller companies
How Virtual Reality works and its Components?
The primary subject of virtual reality is simulating the vision. Every headset aims to perfect their approach to creating an immersive 3D environment. Each VR headset puts up a screen in front of eyes thus, eliminating any interaction with the real world. Two autofocus lenses are generally placed between the screen and the eyes that adjust based on individual eye movement and positioning. The visuals on the screen are rendered either by using a mobile phone or HDMI cable connected to a PC.
The rendered video is sent from the console or computer to the VR headsets which use either two feeds sent to one display or two LCD displays, one per eye. There are also lenses which are placed between your eyes and the pixels, which is why the devices are often called goggles. In some instances, these can be adjusted to match the distance between your eyes, varying from person to person.
These lenses focus and reshape the picture for each eye and create a stereoscopic 3D image by angling the two 2D images to mimic how each of our two eyes views the world ever-so-slightly differently.
To create a truly immersive virtual reality there are certain prerequisites - a frame rate of minimum 60fps, an equally competent refresh rate and minimum 100-degree field of view (FOV). The frame rate is the rate at which the Graphical Processing Unit can process the images per second, screen refresh rate is the pace of the display to render images, and FOV is the extent to which the display can support eye and head movement.
VR is based on the physical principles of physics where content is created and manipulated by a number of hardware devices and software.
The major hardware components include
- Graphics rendering Computers
- Virtual Reality Headset
- Displays
- Network connections
Applications of Virtual Reality:
The applications for VR is endless. Virtual reality may have been considered an overnight sensation but it has been re-invented under the term virtual environments and is proving to be useful in ways which had never been previously considered.
Medicine:Medicine is one of the biggest beneficiaries with the development of surgery simulation. This is often used as a training aid and enables the surgeon to perform an operation on a ‘virtual patient’ or to see inside the human body. It is also used as a diagnostic tool in that it provides a more detail view of the human body compared to X-rays and scans.
Aviation / Aerospace:Three-dimensional aircraft models can be designed which allows the designer to test their prototype without having to have several versions – which are time-consuming and costly.It is cheaper and easier to make changes to the simulation rather than having to design and build a new aircraft.
Geographical visualization:The integration of real-time data and VR allows traffic management to more easily look at varied layers of transport, while also gaining ability to forecast patterns based on historical or expected patterns.
Weather forecasting:VR experience promises to offer immersive weather news, innovative forecasts and 360-degree video of severe weather events of severe weather events.
Data analysis:Data visualizations through VR makes it easier to recognize patterns within datasets. VR also features different perspectives beyond the two-dimensional images we are typically aware.
Future of Virtual Reality:
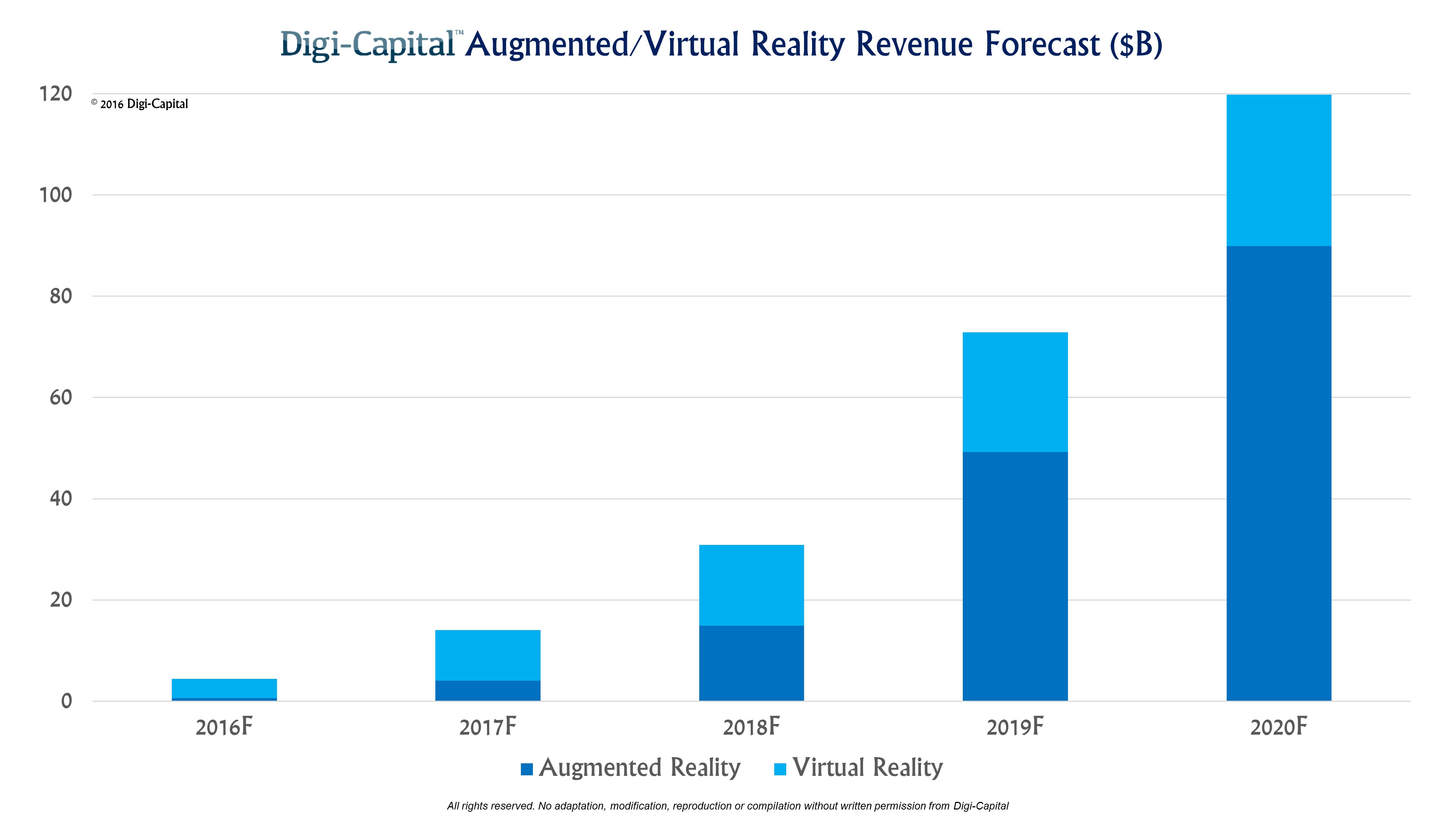
Research firm IDC predicts that the virtual and augmented reality market will dramatically expand from just over $9 billion last year to a whopping $215 billion by 2021! That incredible 118% compound annual growth rate in four years would make VR one of the fastest-growing industries on the planet.
Conclusion:
Virtual Reality is arguably the next footstep towards a modern/post-modern era of development. The potential groundbreaking effects that loom behind these machines is mysterious. With the ability to save lives, act as a medium for business development and confrontations, and provide its users with endless hours of entertainment, learning, and discovery, the world should be pushing for an increased presence of this product, just the same as it did in the 1990’s. This time around, our technology will have come far enough to support the needs for these devices and will begin implementing virtual reality within homes, medical centers, and offices.
About the Author
The writer of this article is a Ph.D. Student & Graduate Teaching Assistant for the Department Of Computer Science at The University of North Dakota.
Sources:https://www.vrs.org.uk/virtual-reality https://whatis.techtarget.com/definition/virtual-reality https://classroom.udacity.com/courses/ud1012 https://www.newgenapps.com/blog/how-vr-works-technology-behind-virtual-reality https://www.wareable.com/vr/how-does-vr-work-explained https://www.fool.com/investing/2018/03/26/what-does-the-future-hold-for-virtual-reality.aspx


















Leave a Reply