DNA is a heredity unit of all living organism on earth. It inherits characters from parents to their generation so it is almost like a memory storage device of all living organism. Taking that as the base, scientists and researchers have been working creating new storage technologies. Data storage in DNA is now a reality and is predicted to be the future of data storage technology.
How does it work – The digital data is encoded in a DNA sequence, the corresponding sequence information is synthesized into an artificial DNA and the information is decoded by sequencing the artificial DNA strand. This is the exact path of storing and retrieving digital data from DNA.
The first form of data which is encoded into DNA was in the form of HTML text template, published by George Church at Harvard University in 2012. This was the first milestone finding in DNA data storage technology.
DNA, INFORMATION AND DATA STORAGE
Basic Comparison of different data storing units :
|
Storage unit |
Storage capacity |
Storage density per mm3 |
|
Magnetic tap |
185 TB |
10GB/mm3 |
|
Optical disc |
1PB |
100GB/mm3 |
|
DNA sequence |
>1XB |
1EB/mm3 |
Process of DNA - Data Storage work
Encoding data into the DNA sequence:
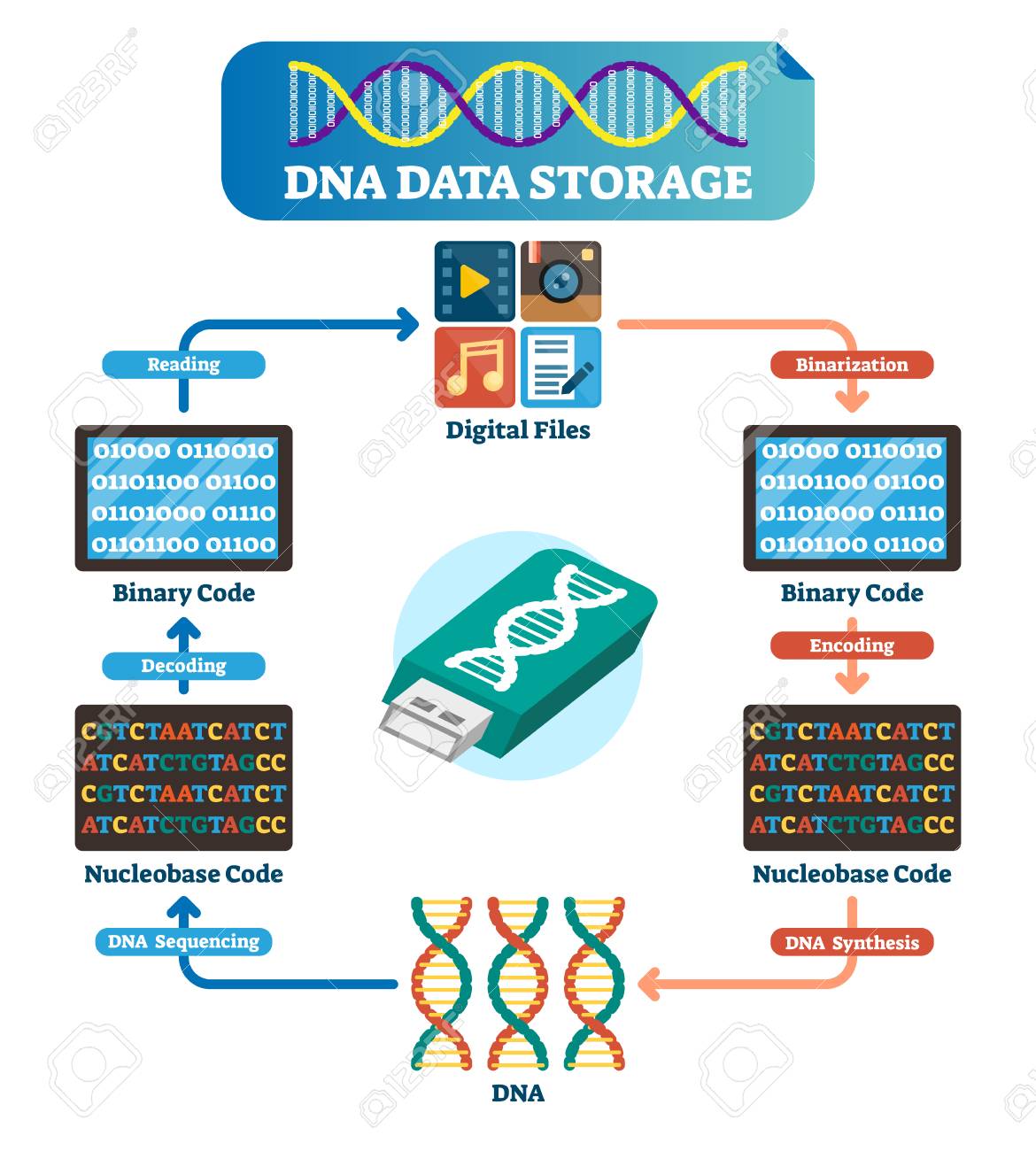 The computer is worked on a binary system of 1 and 2. In the very first step, digital data is incorporated into the DNA. The DNA has 4 nitrogenous bases: Adenine (A), Cytosine (C), Guanine (G) and Thymine (T). For storing data into the DNA, the A, T, G and C bases of DNA first converted into binary codes 1 and 0.
The computer is worked on a binary system of 1 and 2. In the very first step, digital data is incorporated into the DNA. The DNA has 4 nitrogenous bases: Adenine (A), Cytosine (C), Guanine (G) and Thymine (T). For storing data into the DNA, the A, T, G and C bases of DNA first converted into binary codes 1 and 0.
00 for A, 01 for G, 10 for C and 11 for T are the binary codes for storing information. The information in the binary form is converted into the sequence of A, T, G, C. Now we have the long digital sequence of DNA.
Artificial DNA synthesis:
The single-stranded arbitrary DNA sequence can be synthesized chemically. On the basis of the digital sequence data, each nucleotide is added to the adjacent nucleotide. However, the efficiency of artificial DNA synthesis is 99% but the error of 1% can create a major problem in digital data storage.
To overcome this problem, large numbers of parallel start sites are provided to produce multiple copies of the given sequence. Thus, despite having an error in a single copy many other exact copies can be produced.
Storing of sample:
Now we have our data backup in the form of a liquid drop of several nanograms of DNA. The DNA can be stored in deep freeze where it can be last for 100 years or we can send it to the external storage systems (provided by some companies) which can store our DNA for more than thousand years.
DNA remains stable in any harsh conditions for millions of year. Nonetheless, some sequences could be lost over a period of time.
Sequencing of DNA:
For extracting the digital data back to its original form, we have to sequence the entire DNA. DNA sequencing is a process in which a DNA sequence is read into the digital sequence. The labelled nucleotides are added complementary to our DNA strand. Each nucleotide is labelled with a different fluorescent dye. The intensity of colour emitted by each dye is recorded by the detector.
The process is repeated for multiple times with different start sites and which gives multiple parallel sequences of our DNA. The sequence which is exactly matched with our DNA is selected and send to the decoder.
Decoding information:
Finally, the sequence gets back to the decoder which decodes the DNA sequence back into binary language. After decoding, we can retrieve our data back.
Comparison of data storage units with respect to access time and durability.
|
Durability |
Data storage unit |
Access time |
|
3 years |
Flash drive |
Mili second |
|
5 years |
HDD (hard disk) |
10 second |
|
Up to 30 years |
Magnetic tape |
1 minute |
|
More than 100 years |
DNA storage |
More than 12 hours |
APPLICATION, LIMITATIONS AND FUTURE TRENDS
APPLICATIONS - DNA digital data storage technique has several tremendous application.
- It is applicable for storing some miscellaneous files such as previous medical records, legal documents and formal records.
- In any conditions, the data stored in DNA can last for more than 10,000 years and it is guaranteed.
- We can also store the entire data in small replicon libraries Because it occupies very little space.
- By creating a DNA achieves in a single room we can store the entire data of the world.
It is a futuristic huge data storing unit, albeit restricted.
LIMITATIONS - The DNA digital data storage system has Limitations
- It takes a lot of time for storing, processing and computing of data.
- On average, the entire process is completed in 3 to 4 days.
- The cost is another major limitation. Around 15MB of data storage cost up to 100,000 dollars.
- It cannot be used as a pen drive or a magnetic tape.
- If we want to extract a specific type of file from the entire DNA archive, then we have to sequence and read the entire DNA data archive.
FUTURE OF DNA DATA STORAGE
As per a recent report published by IndustryARC on the next generation data storage technology market, DNA Storage is projected to attain total worth of $30m by the end of 2016 and is forecast to grow at a CAGR of 50.73% by 2025.
 The scientists of Microsoft research in collaboration with the University of Washington are working on DNA digital data storage.
The scientists of Microsoft research in collaboration with the University of Washington are working on DNA digital data storage. - Tech giant Google already initiated a DNA digital data storage facilities under the brand name of “google genomics”. However, the project is in the beta phase but Microsoft is reportedly buying 10 million strands of DNA for setting up the DNA digital data storage technology.
- Twist Bioscience is now actively involved commercial in DNA digital data storage technology. So far they have created around 2000 exabytes of data and shipped (decoded) approx. 800 exabytes of data.
Although DNA digital data storage technology is costly and time-consuming at present. Still, it will prove to be very useful in the near future. Conclusively, DNA digital data storage will revolutionize the digital technology for sure.







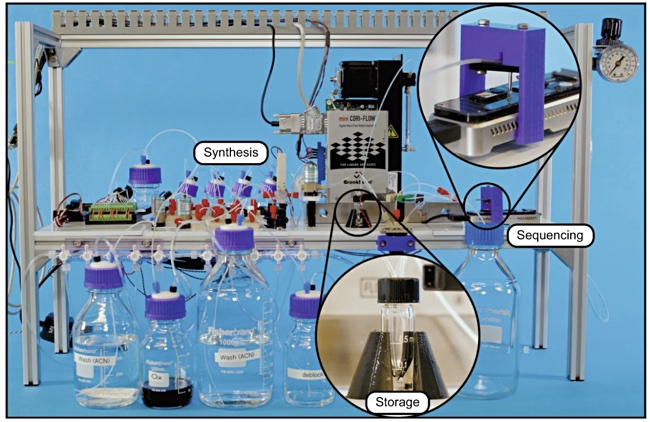 DNA
DNA 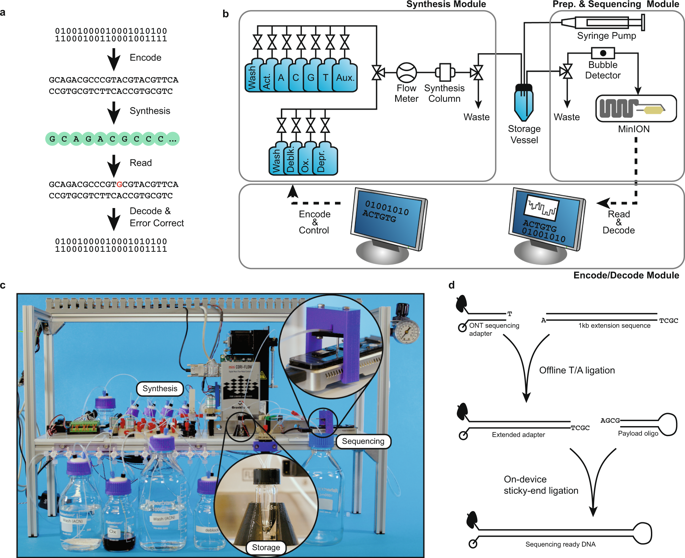











Leave a Reply